J-Spec

Japanese Domestic Market Versions (J-Spec, RHD)
In its home market the Supra had to compete against a variety of different sportscars Japanese manufacturers had in their lineup in the mid 90’s. Almost every brand offered turbo-charged, high-torque engines.
Mitsubishi launched its four wheel-driven GTO (3000GT) in 1990, Nissan offered the Fairlady Z (300ZX) as part of their lineup, Honda sold its high-tech light-weight mid-engined NSX.
Mazda went the remarkable way and sold its top-of-the-range car, the third-generation Mazda RX-7, exclusively with rotary-engines. The 2-rotor Wankel engine is boosted by two turbines operating sequentially, similar to the system used in the Supra.
All these vehicles deliver a maximum power output limited to ~280PS according to the Gentlemen Agreement. Though officially claimed to have 280PS either the Supra’s power output exceeded all its rivals.
All J-Spec versions are limited to 180kph (112mph) according to a Japanese homologation rule.
In the land of the rising sun it’s more about acceleration and agility rather then top-speed and high average highway-speeds. Therefore the J-Spec 2JZ-GTE is equipped with turbine-blades made from the ceramic high-tech material silicium-nitrite for the sake of engine-responsiveness.
Its low density compared to metallic materials allows the turbochargers to spool faster due their lower moment of inertia.
05.1993-08.1994
E-JZA80-ALMVF – Supra SZ 5MT
E-JZA80-ALPVF – Supra SZ AT
E-JZA80-AJPVF – Supra SZ Aerotop AT
E-JZA80-ALFQZ – Supra RZ 6MT
E-JZA80-ALPQZ – Supra RZ AT
E-JZA80-ALPZZ – Supra GZ AT
E-JZA80-AJPZZ – Supra GZ Aerotop AT

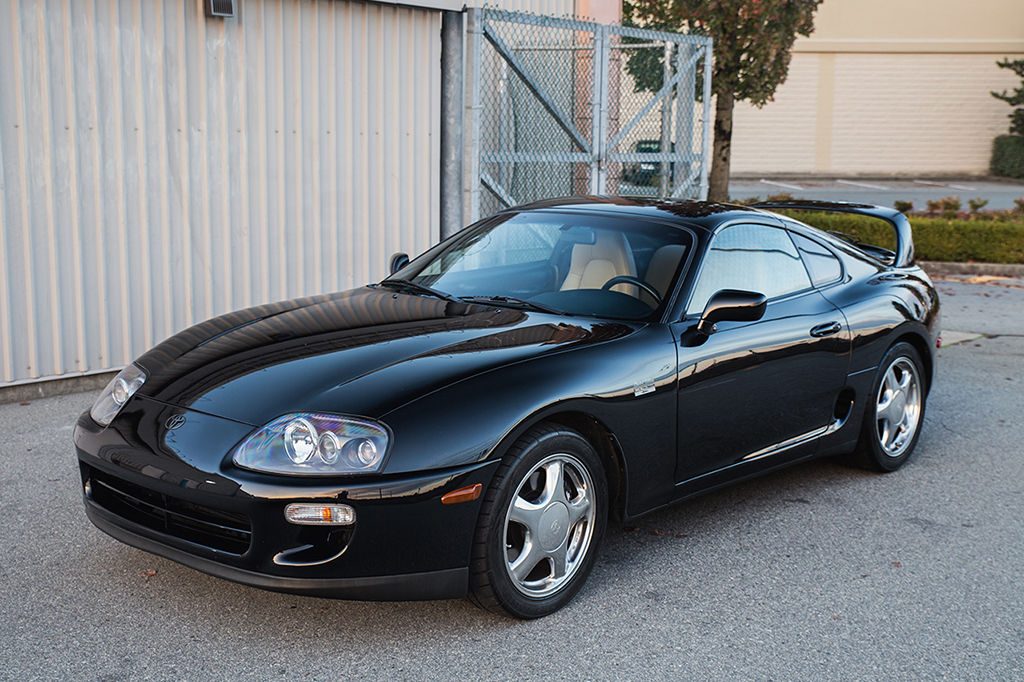
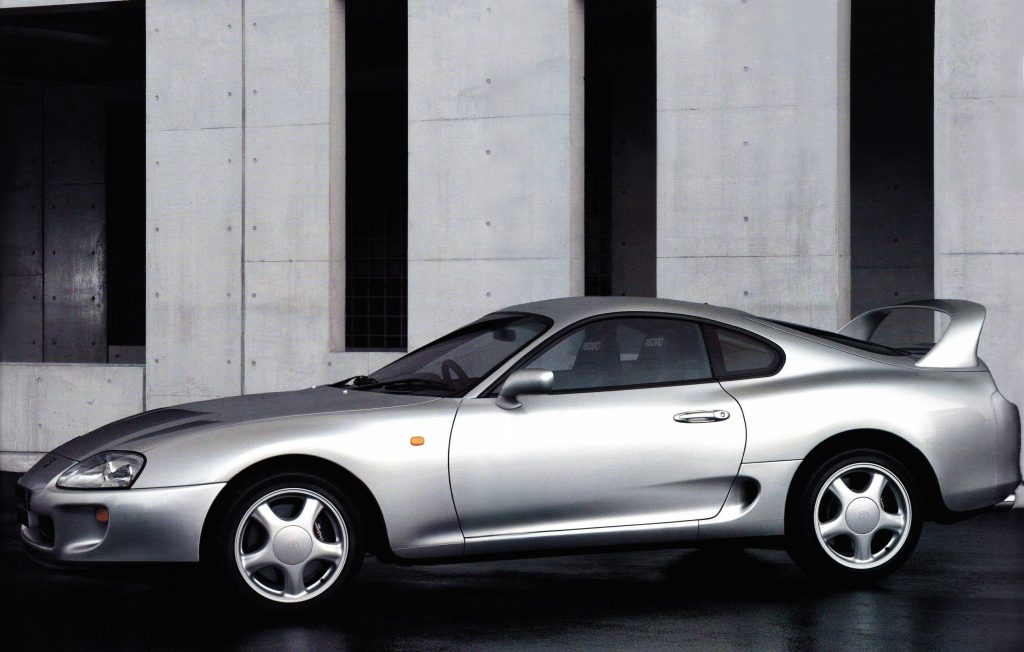
The Supra has been available in 3 different versions when launched in 1993. The Supra SZ has been the entry-level model. It was available with the 2JZ-GE N/A engine, which delivers power either to the 5-speed manual transmission or the 4-speed automatic. ABS and the limited-slip differential were only available for an extra charge.
The medium-level version was the Supra RZ. It comes with the 2JZ-GTE engine connected to the Getrag 6-Speed manual gearbox (LSD standard) or the 4-Speed automatic transmission (LSD optional). The RZ was the only version to come with a Bilstein suspension.

The top-of-the-line version came also with the 2JZ-GTE engine: The Supra GZ has only been delivered with the 4-Speed automatic transmission and LSD. Other luxurious standard equipment details are: Leather Seats, Driver’s Airbag, Cruise Control, active front-spoiler and the Super-Live sound-system with a sub-woofer mounted in the trunk.
These equipment details were optional on SZ and RZ Supras. The passenger airbag was optional to all versions, as well as the large rear-wing.
The targa-roof (“Aerotop”) was available with SZ and GZ equipment grades and only in combination with the automatic transmission.
All versions were equipped with the smaller brake-system together with the 16″-type wheels. The large brake-system with 17″-wheels was not available at all.
08.1994-05.1995
E-JZA80-ALMVF – Supra SZ 5MT
E-JZA80-ALPVF – Supra SZ AT
E-JZA80-AJPVF – Supra SZ Aerotop AT
E-JZA80-ALMSF – Supra SZ-R 5MT
E-JZA80-ALFQZ – Supra RZ 6MT
E-JZA80-ALPQZ – Supra RZ AT
E-JZA80-ALPZZ – Supra GZ AT
E-JZA80-AJPZZ – Supra GZ Aerotop AT
The first model upgrade replaced heated side-mirrors with electrically folding mirrors.

A new equipment grade was added: The Supra SZ-R is a sportier version of the Supra SZ. It was only available with the 5-Speed manual transmission and LSD as standard. ABS and the large rear-wing are standard equipment, too. Furthermore it’s equipped with the Bilstein-Suspension known from the Supra RZ.
SZ, RZ and GZ equipment grades didn’t undergo any changes. The large brake-system was introduced in the Japanese market as optional equipment for GZ and RZ models.
05.1995-04.1996
E-JZA80-ALMVF – Supra SZ 5MT
E-JZA80-ALPVF – Supra SZ AT
E-JZA80-AJPVF – Supra SZ Aerotop AT
E-JZA80-ALMSF – Supra SZ-R 5MT
E-JZA80-ALFQZ – Supra RZ 6MT
E-JZA80-ALFVZ – Supra RZ-S 6MT
E-JZA80-ALPVZ – Supra RZ-S AT
E-JZA80-ALPZZ – Supra GZ AT

The last upgrade before the Facelift in 1996 consisted of various basic changes in the lineup.
The Supra RZ was rebadged as the Supra RZ-S. The Bilstein Suspension was replaced with the standard-type shock absorbers.
The Supra RZ name had been continued and used for the new sporty top-model. The “new” Supra RZ was solely available with the 6-Speed manual transmission and LSD as well as Bilstein shock absorbers as standard equipment. The large rear-wing and Recaro sport-seats were standard equipment, too.
17″-type wheels could be ordered for all models now.
Cruise-Control was completely withdrawn from the equipment list, so did the targa-roof for the Supra GZ versions. It was available on Supra SZ models only from 05.1995 on. A new color was added to the lineup: Dark Green Mica Metallic (6P3).
04.1996-08.1997 (Facelift)
E-JZA80-ALMVF – Supra SZ 5MT
E-JZA80-ALPVF – Supra SZ AT
E-JZA80-AJPVF – Supra SZ Aerotop AT
E-JZA80-ALFSF – Supra SZ-R 6MT
E-JZA80-ALFQZ – Supra RZ 6MT
E-JZA80-ALFVZ – Supra RZ-S 6MT
E-JZA80-ALPVZ – Supra RZ-S AT


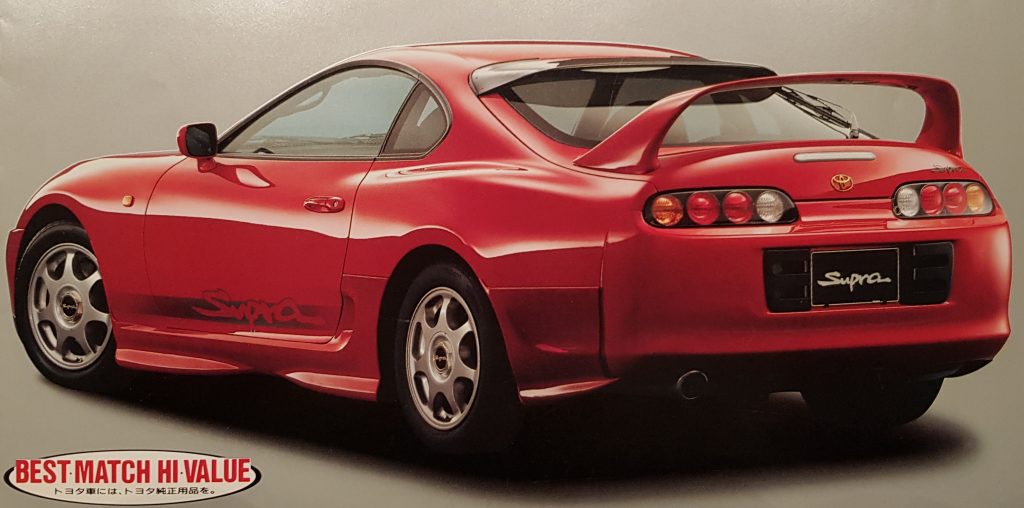
The Supra underwent some cosmetic changes in 1996. Headlight housings were painted black, rear-light clusters changed color to gray. Parking lights were integrated into the front indicator lamps, which got redesigned.
Side indicator-lamps were moved to the sides of the front-skirt to the position of the US-Version’s side marker lamps. The US-Spec version’s red rear side marker lamps were added to the J-Spec version.
The frontal view was upgraded with a horizontal bar in the radiator opening.
Wheel cap design of both 16″ and 17″-type wheels was changed.

The dash panel color changed from black to a light gray, the three large gauges were replaced with two large ones and three small (Fuel, Water Temperature and Boost, respectively Volt-Meter on N/A engine equipped cars). The digital odometer was moved from the center console into the speedometer and changed to an analogue one.
Front seats got an integrated headrest and a new fabric pattern.
GZ-Versions were discontinued. The SZ-R version got the turbo-version’s 6-Speed manual transmission in an upgraded version (V161) as standard equipment and the RZ’s Recaro sport-seats as optional equipment.
Driver and Passenger Airbags became standard equipment on all versions.
The standard 4-channel ABS-System with a lateral deceleration sensor has been replaced by a simpler 3-channel one without this sensor. But SZ-Models did get ABS as standard equipment from 1996 on. The old 4-Channel system was directly replaced by a new “Sport ABS” with a linear deceleration sensor. It was only available in combination with the larger brake system and 17″-Wheels.
Latter became standard equipment on the RZ Supra. Traction Control was upgraded with a “Snow Mode” which is activated with a dash switch.
Paint color Deep Teal Metallic (752) was discontinued. Grayish Green Mica Metallic (6N0) and Blue Mica Metallic (8L5) were introduced.
08.1997-08.2002
E-JZA80-ALMVF (-99) GF-JZA80-ALMVF (99+) – Supra SZ 5MT
E-JZA80-ALPVF (-99) GF-JZA80-ALPVF (99+) – Supra SZ AT
E-JZA80-AJPVF – Supra SZ Aerotop AT (only -99)
E-JZA80-ALFSF (-99) GF-JZA80-ALFSF (99+) – Supra SZ-R 6MT
E-JZA80-ALFQZ (-99) GF-JZA80-ALFQZ (99+) – Supra RZ 6MT
E-JZA80-ALFVZ (-99) GF-JZA80-ALFVZ (99+) – Supra RZ-S 6MT
E-JZA80-ALPVZ (-99) GF-JZA80-ALPVZ (99+) – Supra RZ-S AT
The last time important changes were made was in 1997.

The last time important changes were made was in 1997. While interior modifications were reduced to another new cloth pattern on the standard seats and a 3-Spoke airbag steering-wheel (with carbon-fibre applications on RZ and SZ-R models). RZ-S models were equipped with the same leather-wrapped 6-Speed shift- knob as RZ and SZ-R models. The RZ-S’ steering-wheel became leather-wrapped, too, but without carbon-fibre applications.
Engine-wise much was changed.
The most interesting new feature was the adaption of Toyota’s variable valve-control system VVT-i to the 2JZ-GTE turbo-engine. Variable valve-control on the inlet camshaft resulted on one hand in lower fuel consumption of 12.2 l/100km (8.2km/l according to Japanese industrial standards) and 11.1l / 100km (9.0km/l) in the manual version. On the other hand maximum power ouput was raised to 451Nm.

Together with VVT-i the japanese-version 2JZ-GTE had been equipped with an OBDII-Interface, drive-by-wire throttle control (ETCS-i) and a MAF-Type hot-wire Airflow-Sensor.
Manual turbo-versions got equipped with the upgraded Getrag 6-Speed transmission V161, which had been available on SZ-R Non-Turbo cars earlier.
Automatic turbo-cars were equipped with shift-buttons on the steering-wheel for manual gear change.
Bilstein shock-absorbers on SZ-R and RZ models were replaced by a mechanical-hydraulic system: REAS (Relative Active Absorber) reduces body-roll actively during cornering.
The Supra was sold in this constellation until production ceased in August 2002 due to new emission legislations.
In 1998 a new colour was added to the colour range: Super Bright Yellow. Super Red IV has been replaced by Super Red V in 2001.
Aerotop-Versions were entirely discontinued in August 1999. Simultaneously the model-code changed from E-JZA80 to GF-JZA80 because of the same new emission legislation, which caused end of prdocution in mid 2002.
Complete J-Spec Equipment Overviews
Overview of Japanese Equipment Grades
Alternators
Audio Systems
Brake Systems
Clutches
Differentials
Drive Shafts
Engine Compartment
Exterior
Interior
Radiators
Speakers
Suspension
Transmissions
Technical Specifications
Wheels and Tires